The Critical Role of the Crankshaft in Engine Mechanics
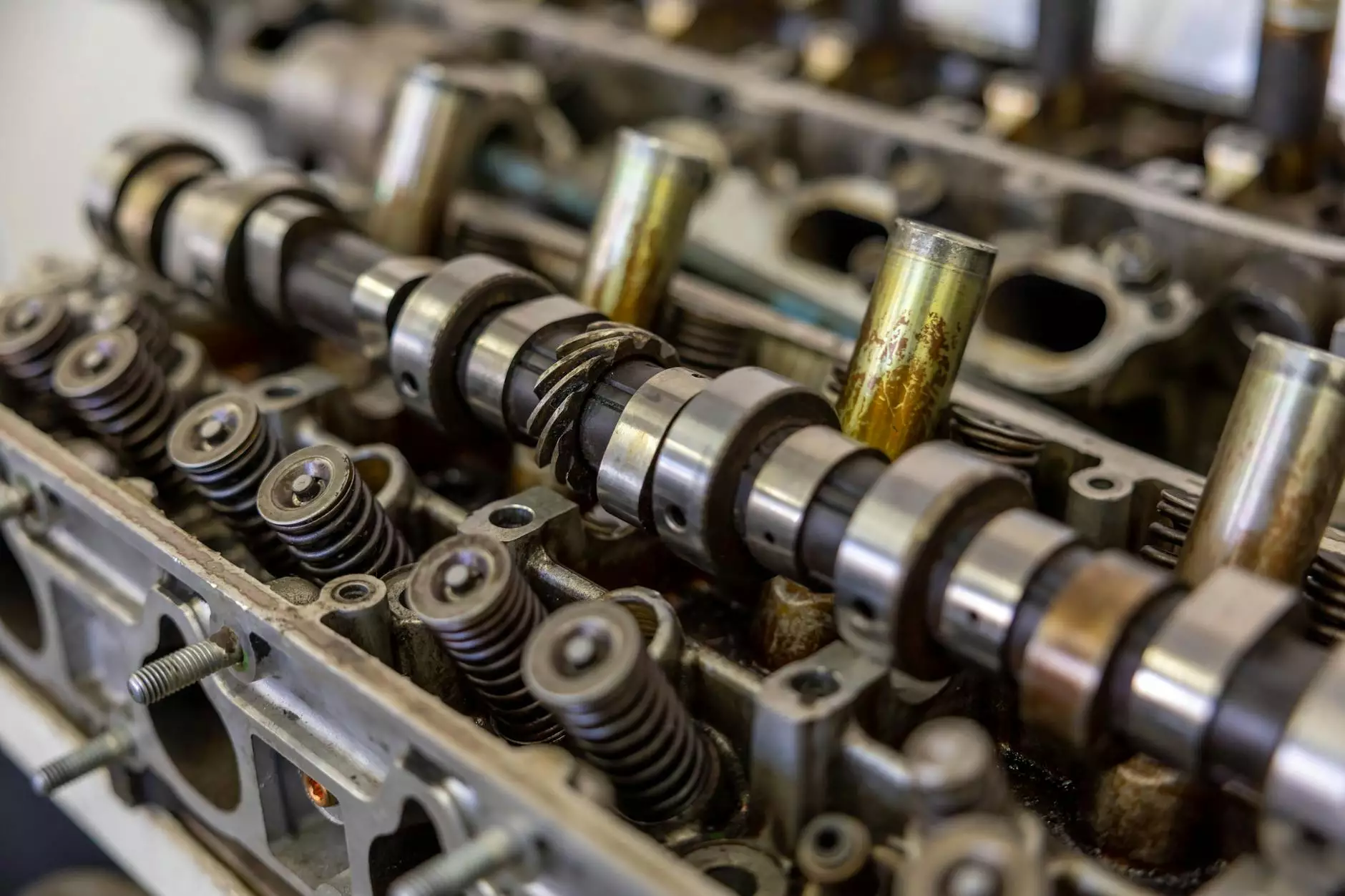

The crankshaft in engine design serves as a fundamental component driving the performance and efficiency of automotive engines, particularly in diesel applications. Understanding the crankshaft's structure and function can significantly contribute to the proper maintenance and optimization of diesel engines. This article delves deeply into the various aspects of the crankshaft, including its components, operation, and importance in the broader context of diesel engine parts and spare parts suppliers.
What is a Crankshaft?
At its core, the crankshaft is a mechanical part that converts the linear motion of pistons into rotational motion. This component is crucial in making the engine's power usable for the vehicle’s movement. Typically found in internal combustion engines, crankshafts are made from high-strength materials designed to endure tremendous forces and rotate at high RPMs.
Components of the Crankshaft
The crankshaft consists of several key components, each playing a vital role in its overall functionality:
- Crank Pins: These are the points where the connecting rods attach, and they are directly responsible for transforming the linear motion of the pistons into a rotary motion.
- Main Journals: These are the smooth, cylindrical areas where the crankshaft rests on the engine block, allowing for smooth rotation.
- Dampers: Attached to the end of the crankshaft, these components help absorb vibrations produced during engine operation.
- Counterweights: They balance the crankshaft, enhancing stability and reducing engine vibrations.
The Function of the Crankshaft in the Engine
The essential function of the crankshaft includes:
- Converting reciprocating motion from the pistons into rotational motion, driving the vehicle's wheels.
- Transferring power from the combustion process to the transmission system, facilitating movement.
- Maintaining engine balance and reducing vibration through its design and counterweights.
Crankshaft Design and Materials
The design of a crankshaft is critical to its performance and durability. Typically, crankshafts are designed with:
- Forged Steel: This material provides superior strength and durability, making it ideal for high-performance applications.
- Cast Iron: Common in many older and less demanding engines, it offers a balance of strength and cost-effectiveness.
- Alloy Components: These may be added to enhance certain properties, such as resistance to wear and fatigue.
Importance of the Crankshaft in Diesel Engines
In diesel engines, the role of the crankshaft is magnified due to the nature of diesel combustion. Diesel engines operate at higher compression ratios, which can exert enormous forces on the crankshaft. Therefore, the crankshaft must be resilient and precisely engineered to handle such stress. Key points include:
- Force Distribution: A well-designed crankshaft evenly distributes forces throughout the engine, preventing premature wear and failure.
- Performance Optimization: The crankshaft's balance and weight distribution can significantly affect engine performance, affecting torque delivery and efficiency.
- Durability: Given the high-stress environment of a diesel engine, crankshafts are designed to withstand wear and tear over extended periods, which is vital for maintenance and reliability.
Common Issues with Crankshafts
Crankshaft Damage and Wear
Despite their robust design, crankshafts can experience various issues over time:
- Wear and Tear: Regular usage can lead to gradual wear, particularly on crank pins and main journals.
- Cracking: Extreme stress or fatigue can lead to cracks in the crankshaft, which can cause catastrophic engine failure.
- Misalignment: Improper installation or wear in bearing supports can lead to misalignment, resulting in uneven wear and potential engine damage.
Signs of Crankshaft Problems
Identifying issues early can prevent extensive engine damage. Key signs include:
- Vibrations: Excessive vibrations during operation could indicate imbalance or wear.
- Knocking Noises: Unusual noises that arise upon starting or accelerating may signify internal damage.
- Oil Leaks: Leaks around the crankshaft seal can point to wear or damage.
Maintenance of the Crankshaft
Maintaining the crankshaft is crucial for ensuring long-lasting engine health. Recommended practices include:
- Regularly changing engine oil to minimize contaminants that can lead to wear.
- Caring for your heating and cooling systems to prevent overheating, which can affect crankshaft integrity.
- Being vigilant for any signs of wear or unusual noises and addressing them immediately.
Choosing the Right Replacement Crankshaft
When it comes to replacing a crankshaft, especially in diesel engines, quality cannot be compromised. Here are some tips for making the right choice:
- OEM vs. Aftermarket: Consider original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts for guaranteed performance and compatibility.
- Material Quality: Ensure that the new crankshaft is made from high-quality materials adequately rated for your engine's performance requirements.
- Supplier Reputation: Work with trusted spare parts suppliers, like client-diesel.com, known for quality and reliability in diesel engine parts.
Conclusion: The Crankshaft's Indispensable Role
The crankshaft in engine operation is integral to understanding the overall functionality and performance of diesel engines. Proper maintenance, immediate addressing of issues, and investment in quality replacements are essential steps in maximizing engine life and performance. By recognizing the crankshaft's vital role, owners can ensure optimal operation and reliability of their diesel engines, paving the way for efficient service and reduced operational costs.
For high-quality diesel engine parts and knowledgeable spare parts suppliers, consider exploring the offerings at client-diesel.com. Ensuring your equipment has the finest components will keep your engines running efficiently and robustly.